Mixed Crossflow Evaporative Fluid Cooler
Mixed Crossflow Evaporative FluidCooler is used to Cool the hot water or other Fluid .Water or fluid is re-circulated in the unit, moving across the coil with coolant. A fan forces fresh air up through the coil. The process transfers heat from the coolant to the circulating water where it is rejected into the space through evaporation.
Evaporative Fluid coolers eliminate the need for a heat exchanger between the process loop and the heat rejection equipment. Unlike a cooling tower, where process water is used as the energy transfer medium and is open to the atmosphere, the coil inside a closed-circuit cooler isolates the process fluid.
In a closed circuit cooler, process fluid is circulated through coils within the unit. A water distribution system cascades water over the tubes of the coil, extracting heat from the process loop via evaporation. Air is drawn or forced across the coils, agitating the falling water and increasing the transfer of heat. A small amount of this water evaporates due to latent heat transfer through the tube and fin walls of the coil, removing heat from the system. The cooled process fluid returns to the building via the bottom coil connection. Cascaded water drains to a basin and is recirculated back over the coil.
These coolers provide energy-efficient operation in a reduced footprint compared to dry coolers, due to evaporation being used as the primary method of cooling. Because blowdown of the basin water is reduced on closed-loop systems, water conservation is also improved when compared to open-loop systems. Because evaporative coolers can oftentimes run dry when ambient conditions are favorable during reduced load conditions, water consumption is eliminated entirely during these periods of operation.

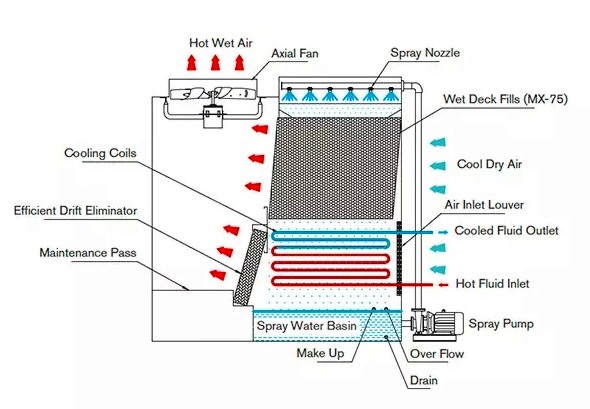
Working Theory
Mixed Crossflow Evaporative FluidCooler belongs to induced draft type cross flow cooling towers. During the working process, dry cool air is inlet through wide louvers on one side of the tower, then directed through the heat exchange coils and wet deck fills across the spray water, becoming wet hot air, eventually induced draught out of the tower into the atmosphere by the fans on the top. In this process, a part of heat from the fluids inside the closed loop is transferred efficiently, and removed continuously.
More Images of Mixed Crossflow Evaporative Fluid Cooler
Material of Construction
| Component | Material Options |
|---|---|
| Heat Exchanger Coil | SS 304, SS 316, Carbon Steel, Hot Dip Galvanized Steel, Copper |
| Side Covers | SS 304, SS 316, Carbon Steel, Hot Dip Galvanized Steel |
| Internal Structures | SS 304, SS 316, Carbon Steel, Hot Dip Galvanized Steel |
| Fill Media | PVC |
| Fan | Aluminum, FRP, PAG |
Product Features
- Suitable for cooling process water, glycol-water solutions, oil, chemicals, pharmaceutical liquids, machine cooling acids, and other process fluids
- Modular construction enables plug & play installation for both new and replacement units
- Operational cost savings compared to conventional systems
- Zero contamination prevents algae formation
- Suitable for lower approach temperatures and varied temperature differences
- Provides field-erected units and turn-key solutions, including balance of plant supply
Advantages
- Capable and flexible in providing customized solutions
- Factory assembled for maximum installation convenience
- Modular design suitable for a wide range of heat rejection duties
- Compact design with minimal footprint
- Multiple corrosion-resistant options available
- Low sound operation options available
- Additional optimizing options available
- Guaranteed performance and quality
- Extremely long service life
