Forced Draft Cooling Towers
Forced Draft Cooling Towers is a type of cooling tower fan is used to circulate the air. When power plant runs on peak load, it requires a very high rate of cooling water. To rotate fan, it uses motor with speed around 1000 rpm. Working principle is same as natural draught cooling tower, only difference is that here fan is mounted on the cooling tower. If fan is mounted on the top of the tower is called as induced draught cooling tower which is most popular for very large capacity installation and requires large capacity of fan. So, Forced Draught Cooling Towers contains horizontal shaft for the fan and it is placed at bottom of the tower and induced draught cooling tower contains vertical shaft and it is placed at top of the cooling tower.

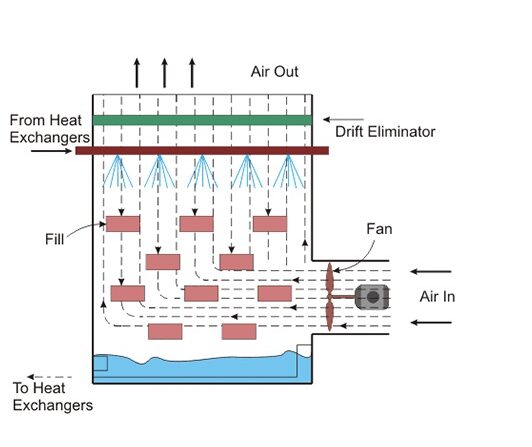
Structural Diagram
The forced draft cooling towers remove low-potential heat generated in the production process. They use atmospheric cooling with wet technology and forced draft. A counterflow of air and hot water in the cooling fill results in a heat transfer. The air flow is provided by a propeller fan while the drift eliminators prevent the transfer of small the tower space.
More Images of Forced Draft Cooling Tower
Components
- Outer shell (material: FRP, steel, stainless steel, concrete)
- Supporting structure
- Fan stack
- Cooling fill
- Drift eliminators
- Fan with drive
- Water distribution system including spraying nozzles
- Water basin
Advantages
- More efficient than induced draught
- No problem of fan blade erosion because it handles dry air only
- More safe
- The vibration and noise are minimum
Application
- Energy industries
- Petrochemical industry
- Chemical industry
- Engineering industry and metallurgy
- Mining industry
- Plastic and rubber industry
- Paper industry
- Manufacturing industry (food processing, sugar refineries)
